场景题
题一:最高得分
一个长度为$N$的序列,玩家每次只能从头部或尾部拿数字,不能从中间拿。拿走的数字依次从左到右排列在自己面前。拿完$N$个数字之后,游戏结束。此时$N$个数字在玩家面前组成一个新的排列,这个数列每相邻两个数字之差的绝对值之和为玩家最终得分。假设玩家前面的$N$个数字从左到右标号为 $n_1,n_2, \dots, n_N$,则最终得分$S$的计算方式如下:
$$
S = \text{abs}(n_1-n_2) + \text{abs}(n_2-n_3) + \cdots + \text{abs}(n_{N-1} - n_N).
$$
请计算玩家在以上游戏规则中把所有数字拿完可以获得的最大得分。
思路:拿到这个问题,感觉像是动态规划。得想办法把子问题拆出来。但是一般情况下,并不是这么好拆的。所以从最简单的用例开始。假设只有两个数,这很简单,无论怎么拿,得分都一样。再加一个数呢?你就要考虑从哪里先拿,然后再从哪里先拿的问题。假设现在有三个数,你从前端拿了一个数,则下一步你得考虑从哪里拿的增益比较大。从前端拿得到一个 front_gain,从末端拿得到一个 back_gain. 你得比一比哪个会让你的得分最大化。然后下一步继续这样考虑,这就形成了一个递归步。就是说你已经拆出来了!专业店说就是你找除了递推关系式。
题外话:Case analysis is more powerful than you thought!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| #include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
/**
* @breif Calculate the max score of the given array.
* @param arr The origin array.
* @param beg The begining of the range.
* @param end The end of the range.
* @param isFront Is the last taken from the front or not.
* @return The max score in a paticular setting.
*
* Note that the @c arr is the origin array, and [beg, end)
* range is considered from the second step, with @c isFront.
* For example:
* Suppose @c arr.size() = 5
* If @c isFront = true, means the last taken is from the front,
* then [beg, end) = [1, 5).
* If @c isFront = false, means the last taken is from the back,
* then [beg, end) = [0, 4).
*/
int opt(const vector<int>& arr, int beg, int end, bool isFront) {
// base cases
if (beg >= end) return 0;
if (end - beg == 1) {
if (isFront)
return abs(arr[beg] - arr[beg-1]);
else
return abs(arr[beg] - arr[end]);
}
// ELSE
int front_gain = 0; // the gain if take front at current step
int back_gain = 0; // the gain if take back at current step
if (isFront)
{
front_gain = abs(arr[beg] - arr[beg-1]);
back_gain = abs(arr[end-1] - arr[beg-1]);
}
else
{
front_gain = abs(arr[beg] - arr[end]);
back_gain = abs(arr[end-1] - arr[end]);
}
return max(
front_gain + opt(arr, beg+1, end, true),
back_gain + opt(arr, beg, end-1, false));
}
int main()
{
int N = 0;
cin >> N;
vector<int> arr;
for (int i=0; i!=N; ++i)
{
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
arr.push_back(tmp);
}
int maxwin = max(
opt(arr, 1, arr.size(), true),
opt(arr, 0, arr.size()-1, false));
cout << maxwin;
return 0;
}
|
题二:最少硬币
2019 腾讯实习生笔试题
小 Q 去商场购物,经常会遇到找零钱的问题。小 Q 现在手上有$n$种不同面值的硬币,每种面值的硬币有无限多个。为了方便购物,小 Q 希望带尽量少的硬币,并且要能组合出$1$到$m$之间(包含$1$和$m$)的所有面值。
输入描述:
第一行包含两个整数$m, n ~(1 \le n \le 100, ~1 \le m \le 10^9)$,含义如题所述。
接下来$n$行,每行一个整数,每$i+1$行的整数表示第$i$种硬币的面值。
输出描述:
输出一个整数,表示最少需要携带的硬币数量。如果无解,则输出$-1$.
示例输入:
20 4
1
2
5
10
示例输出:
5
思路:一拿到就让人联想到动态规划。但其实不是,因为它的条件是要构成所有 1 到 m 之间的面值。所以就得从 1 到 m 慢慢凑出来。假设当前选择的硬币已经可以构成 [1, i], 那么我当然下次在选面值的之后,会很理想的去寻找一个面值为 i+1 的硬币。这样我可以使我构造的最大面值尽可能的大。如果这个面值大于 m 了,那我们就完事儿了。这是贪心的思想。具体来说,比方已选的硬币可以构造出 1 到 5 之间的任何面值,那我在选择一个面值为 6 的硬币,就可以构造出 1 到 11 之间的任何面值。所以我们从面值为 1 的开始加,记录当前可以构造的最大面值 max_constructed,在选择下一个硬币的时候,优先选择面值<=max_constructed+1 的硬币。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/MOU_IT/article/details/89057036
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int MinimalCoin(const vector<int>& coins, int amount)
{
if (coins.empty())
throw std::invalid_argument("empty coins");
if (coins[0] != 1)
return -1;
int max_constructed = 0;
int cnt = 0;
do
{
for (int n = coins.size() - 1; n >= 0; --n)
{
if (coins[n] <= max_constructed + 1)
{
max_constructed += coins[n];
++cnt;
break;
}
}
} while (max_constructed < amount);
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
// address input
int n, m;
cin >> m >> n;
int val;
vector<int> coins;
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i)
{
cin >> val;
coins.push_back(val);
}
std::sort(coins.begin(), coins.end());
cout << MinimalCoin(coins, m);
return 0;
}
|
题三:进制转换
2019 哈罗单车实习生笔试题
将一个 10 进制整数转换成 36 进制的数,可以用 0-9A-Z 表示 0-35.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| /**
* Hellobike 2019 interview.
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string itob36(int n) {
int r = 0; // remainder of n mod 36
string tmp;
// iteratively divde by 36 to get each digit
while (n) {
r = n % 36;
tmp += MAP[r];
n /= 36;
}
// reverse tmp to ret
string ret;
cout << "tmp is " << tmp << endl;
for (auto iter = tmp.rbegin(); iter != tmp.rend(); ++iter)
ret.push_back(*iter);
return ret;
}
private:
string MAP[36] = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", \
"6", "7", "8", "9", "A", "B", \
"C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", \
"I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", \
"O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", \
"U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z"};
};
// test
int main() {
int number = 12345;
cout << Solution().itob36(number);
return 0;
}
|
题四:舞会
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/9efe02ab547d4a9995fc87a746d7eaec
来源:牛客网
今天,在冬木市举行了一场盛大的舞会。参加舞会的有 n 位男士,从 1 到 n 编号;有 m 位女士,从 1 到 m 编号。对于每一位男士,他们心中都有各自心仪的一些女士,在这次舞会中,他们希望能与每一位自己心仪的女士跳一次舞。同样的,对于每一位女士,她们心中也有各自心仪的一些男士,她们也希望能与每一位自己心仪的男士跳一次舞。在舞会中,对于每一首舞曲,你可以选择一些男士和女士出来跳舞。但是显然的,一首舞曲中一位男士只能和一位女士跳舞,一位女士也只能和一位男士跳舞。由于舞会的时间有限,现在你想知道你最少需要准备多少首舞曲,才能使所有人的心愿都得到满足?
input:
第一行包含两个整数 n,m,表示男士和女士的人数。1≤n,m≤ 1000
接下来 n 行,
第 i 行表示编号为 i 的男士有 ki 个心仪的女生
然后包含 ki 个不同的整数分别表示他心仪的女士的编号。
接下来 m 行,以相同的格式描述每一位女士心仪的男士。
output:
一个整数,表示最少需要准备的舞曲数目。
示例输入:
3 3
2 1 2
2 1 3
2 2 3
1 1
2 1 3
2 2 3
示例输出:
2
说明:
对于样例 2,我们只需要两首舞曲,第一首舞曲安排(1,1),(2,3),(3,2);第二首舞曲安排(1,2),(2,1),(3,3)。
思路:乍一看好象很难,不知道怎么处理。其实只要仔细看清楚题目要求:要求每个刃都能得到满足!这很重要,即便还有一个我喜欢的人没跟我跳,就得再放一首歌让我跳!了解到这个需求之后,问题就变的简单了,只要统计出每个人心仪人的数量,以及被心仪的数量,对所有人求一个最大值就行了。
参考:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/9efe02ab547d4a9995fc87a746d7eaec
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
int main()
{
// read input and built heartbeat matrix
int num_men, num_women, num_likes, val;
std::cin >> num_men >> num_women;
int total_num = num_men + num_women;
// the heartbeat matrix
vector<vector<int> > mat(total_num, vector<int>(total_num, 0));
for (int i = 0; i != total_num; ++i)
{
std::cin >> num_likes;
while (num_likes--)
{
std::cin >> val;
if (i < num_men) // man to woman
mat[i][val+num_men-1] = 1;
else // woman to man
mat[i][val-1] = 1;
}
}
// done
// count for each persons hearbeats
int songs_needed = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != total_num; ++i)
{
int cnt = 0;
if (i < num_men) // counting for each man
{
for (int j = num_men; j != total_num; ++j)
{
if (mat[i][j] == 1) // man i like woman j
++cnt;
else if (mat[j][i] == 1) // man i is liked by woman j
++cnt;
}
}
else
{
for (int j = 0; j != num_men; ++j)
{
if (mat[i][j] == 1)
++cnt;
else if (mat[j][i] == 1)
++cnt;
}
}
if (songs_needed < cnt) songs_needed = cnt; // update songs if needed
}
std::cout << songs_needed;
return 0;
}
|
题五:输出数组的全排列
给定一个数组,求其全排列。
Idea: pick one element as prefix, then add to the permutations of the rest n-1 elems.
Reference: https://www.cnblogs.com/ranjiewen/p/8059336.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| #include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
void Permute(int arr[], int beg, int end)
{
if (beg == end)
{
std::copy(arr, arr + end, std::ostream_iterator<int>(std::cout));
std::cout << std::endl;
}
for (int i = beg; i != end; ++i)
{
std::swap(arr[i], arr[beg]);
Permute(arr, beg + 1, end);
std::swap(arr[i], arr[beg]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
Permute(arr, 0, 5);
return 0;
}
|
题六:斜线填充
给定 n x m 的矩阵,按照从右上往左下的斜线填充 1 到 n*m 的值。
例如,对于一个 3x3 的矩阵,
1 2 4
3 5 7
6 8 9 (3x3)
1 2 4 7
3 5 8 10
6 9 11 12 (3x4)
思路:干就完了。先填充左上角的三角区域,再填充右下角的三角区域。注意边界条件,无论行或列到达边界,记得跳转。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
Solution(int n, int m)
{
// fill with 0
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i)
mat.push_back(vector<int>(m, 0));
}
void skewFill(int n, int m)
{
int cnt = 1;
// fill the up-left triangle
for (auto col = 0; col != m; ++col)
{
for (auto i = 0, j = col; i != n && j >= 0; ++i)
mat[i][j--] = cnt++;
}
// fill the bottom-right triangle
for (auto row = 1; row != n; ++row)
{
for (auto j = m-1, i = row; i != n && j >= 0; ++i)
mat[i][j--] = cnt++;
}
}
/// print the matrix
void printer()
{
for (auto &row : mat)
{
for (auto &col : row)
printf("%3d ", col);
cout << endl;
}
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> mat;
};
// test
int main()
{
int n = 0, m = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
Solution s(n, m);
s.skewFill(n, m);
s.printer();
return 0;
}
|
题七:螺旋矩阵
按顺时针填充螺旋填充矩阵。例如:
9 8 7
2 1 6
3 4 5 (3x3)
12 11 10 9
3 2 1 8
4 5 6 7 (3x4)
Idea: Imagine there are for borders that surround the matrix. We walk through the mat, and once achieve a border, we change the direction. Each time we finished a circle, we will shrink our border, and start next circle. After we fill (row * col) elems in the matrix, we are done!
Note: this solution is the most elegant in my opinion, for it’s simple boundray case.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
class Solution
{
public:
Solution(int rows, int cols)
: mat_(rows, vector<int>(cols, 0))
{
}
void BuildMat()
{
// 4 border
int top = 0;
int bot = mat_.size() - 1;
int left = 0;
int right = mat_[0].size() - 1;
int N = (bot + 1) * (right + 1);
for (int i = 0, j = 0; N != 0; --N)
{
// make sure fill exactly one element at each loop
mat_[i][j] = N;
if (i == top)
{
if (j < right) ++j; // go right
else if (j == right) ++i; // checkpoint
}
else if (j == right)
{
if (i < bot) ++i; // go down
else if (i == bot) --j;
}
else if (i == bot)
{
if (j > left) --j; // go left
else if (j == left) --i;
}
else if (j == left)
{
if (i > top + 1) --i; // go up
else if (i == top + 1)
{
++j;
// shrink borders
++top, --bot, ++left, --right;
}
}
else
{
throw std::runtime_error("not behaved expectedly");
}
}
}
void Print()
{
for (auto &r : mat_)
{
for (auto &c : r)
printf("%2d ", c);
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
private:
vector<vector<int> > mat_;
};
// test
int main()
{
Solution so(3, 4);
so.BuildMat();
so.Print();
return 0;
}
|
题八:点击窗口的索引
网易雷火游戏 2019 校招
本题需要让你模拟一下在 Windows 系统里窗口和鼠标的点击操作,具体如下:
- 屏幕分辨率为 3840x2160,左上角坐标为 (0, 0),右下角坐标为 (3839, 2159).
- 窗口是一个矩形的形状,由左上角坐标 (x, y), 和宽高 (w, h) 四给数字来定位。左上角坐标为 (x, y), 右下角坐标为 (x+w, y+h). 其中左上角坐标一定会在屏幕范围内,其他一些部分可能会超过屏幕范围。
- 窗口的点击和遮挡规则同 Windows,但是不考虑关闭窗口、最大化、最小化和强制置顶的情况。即,
- 如果发生重叠,后面打开的窗口会显示在前面打开的窗口上面
- 当鼠标发生一次点击的时候,需要判断点击到了哪个窗口,如果同个坐标有多个窗口,算点击到最上层的那个
- 当一个窗口被点击的时候,会浮动到最上层
输入描述:
每个测试输入包含 1 个测试用例。第一行为 2 个整数 N,M。其中 N 表示打开窗口的数目,M 表示鼠标点击的数目,其中$0<N,M < 1000$.
接下来 N 行,每一行四个整数$x_i, y_i, w_i, h_i$, 分别表示第 i 个窗口(窗口 id 为 i,从 1 开始计数)的左上角坐标以及宽高,初始时窗口是按输入的顺序依次打开。其中$0 \le x_i < 3840$, $0 \le y_i < 2160$, $0 < w_i < 3840$, $0 < h_i < 2160$.
再接下来有 M 行,每一行两个整数$x_j, y_j$, 分别表示接下来发生的鼠标点击坐标。其中$0 \le x_j < 3840, ~0 \le y_j < 2160$
输出描述:
对于每次鼠标点击,输出本次点击到的窗口 id。如果没有点击到窗口,输出 -1.
示例输入:
2 4
100 100 100 100
10 10 150 150
105 105
180 180
105 105
1 1
示例输出:
2
1
1
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
| #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// global const
enum {
WIDTH = 3840,
HEIGHT = 2160
};
// abstraction for 2D point
struct Pos
{
int x;
int y;
Pos(int xx, int yy): x(xx), y(yy)
{
}
};
// abstraction for window
struct Window
{
int id;
Pos point;
int width;
int height;
Window(int idx, int x, int y, int w, int h)
: id(idx), point(x, y), width(w), height(h)
{
}
};
/// is the point @c p in the window @c w
bool IsInWindow(const Window& w, const Pos& p)
{
int left = w.point.x;
int right =
(left + w.width < WIDTH) ? (left + w.width) : WIDTH-1;
int top = w.point.y;
int bot =
(top + w.height < HEIGHT) ? (top + w.height) : HEIGHT-1;
if (p.x >= left && p.x <= right)
{
if (p.y >= top && p.y <= bot)
return true;
}
return false;
}
/// which window do i click on
int ClickWhich(vector<Window>& windows, const Pos& click)
{
// 窗口叠放次序,从上层到下层
for (int i = windows.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
if (IsInWindow(windows[i], click))
{
int ret = windows[i].id + 1;
windows.push_back(windows[i]);
windows.erase(windows.begin() + i);
return ret;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int num_open_windows, num_clicks;
cin >> num_open_windows >> num_clicks;
// read windows
vector<Window> windows;
for (int i = 0, x,y,w,h; i != num_open_windows; ++i)
{
cin >> x >> y >> w >> h;
windows.emplace_back(i, x, y, w, h);
}
// read clicks
vector<Pos> clicks;
for (int i = 0, x,y; i != num_clicks; ++i)
{
cin >> x >> y;
clicks.emplace_back(x, y);
}
// io done
for (auto &e : clicks)
{
cout << ClickWhich(windows, e) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
题九:Stern-Brocot Tree
网易雷火游戏 2019 校招
The Stern-Brocot tree is an infinite complete binary tree in which the verices correspond one-for-one to the positive rational numbers, whose values are ordered from the left to the right as in a search tree.

Figure above shows a part of the Stern-Brocot tree, which has the first 4 rows. The value in the node is the mediant of the left and right fractions. The mediant of two fractions A/B and C/D is defined as (A+C)/(B+D).
To construct the Stern-Brocot tree, we first define the left fraction of the root node is 0/1, and the right fraction of the root node is 1/0. So the value in the root node is the mediant of 0/1 and 1/0, which is (0+1)/(1+0)=1/1. Then the value of root node becomes the right fraction of the left child, and the left fraction of the right child. For example, the 1st node in row2 has 0/1 as its left fraction and 1/1(which is the value of its parent node) as its right fraction. So the value of the 1st node on row2 is (0+1)(1+1)=1/2. For the same reason, the value of the 2nd node in row2 is (1+1)/(1+0)=2/1. This construction progress goes on infinity. As a result, every positive rational number can be found on the Stern-Brocot tree, and can be found only once.
Give a rational nunmber in form P/Q, find the position of P/Q in the Stern-Borcot tree.
Input description:
Input consists of two integers, P and Q (1<=P,Q <= 1000), which represent the rational number P/Q. We promise P and Q are relatively prime.
Output description:
Output consists of two integers, R and C. R indicates the row index of P/Q in the Stern-Brocot tree, C indicates the index of P/Q in that row.
Both R and C are base 1. We promise the position of P/Q is always in the first 12 rows of the Stern-Brocot tree, which means R<=12.
Sample input:
5 3
Sample output:
4 6
Idea: tree structure is natural for recursion.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
// build Rat abstraction
typedef std::pair<int, int> Rat; // the rational numbers
Rat operator+(const Rat& lhs, const Rat& rhs)
{
// 事实上这里需要化简使得分子分母互素
// 不过下面我判断等于的时候是交叉相乘判断的,故不影响结果
return std::make_pair(
lhs.first + rhs.first,
lhs.second + rhs.second);
}
bool operator<(const Rat& lhs, const Rat& rhs)
{
return (lhs.first * rhs.second)
< (rhs.first * lhs.second);
}
bool operator>(const Rat& lhs, const Rat& rhs)
{
return !(lhs < rhs);
}
bool operator==(const Rat& lhs, const Rat& rhs)
{
return (lhs.first * rhs.second)
== (rhs.first * lhs.second);
}
void Printer(const Rat& r)
{
cout << r.first << "/" << r.second << endl;
}
// done
struct SBTreeNode
{
Rat LF; // left fraction
Rat val;
Rat RF; // right fraction
SBTreeNode(Rat l, Rat v, Rat r)
: LF(l), val(v), RF(r)
{
}
};
/// search the SBTree for target, return the row and col index
void SearchOnTree(
SBTreeNode& root, const Rat& target, int* prow, int* pcol)
{
// base case
if (target == root.val) return;
// 可以看到 Stern-Brocot 树具有二叉排序树的特征
// left-child < parent < right-child
if (target < root.val)
{ // go left
root.RF = root.val;
root.val = root.val + root.LF;
++(*prow);
*pcol = (*pcol) * 2 - 1;
SearchOnTree(root, target, prow, pcol);
}
else if (target > root.val)
{ // go right
root.LF = root.val;
root.val = root.val + root.RF;
++(*prow);
(*pcol) *= 2; // 注意列索引的增量,仔细看规律
SearchOnTree(root, target, prow, pcol);
}
}
int main()
{
Rat query;
cin >> query.first >> query.second;
SBTreeNode root(Rat(0,1), Rat(1,1), Rat(1,0));
// root.RF = root.val;
// root.val = root.val + root.LF;
// cout << "LF "; Printer(root.LF);
// cout << "val "; Printer(root.val);
// cout << "RF "; Printer(root.RF);
int row = 1, col = 1;
SearchOnTree(root, query, &row, &col);
cout << row << " " << col << endl;
return 0;
}
|
题十:解码字符串
腾讯 2019 校招
小 Q 想要给他的朋友发送一个神秘的字符串,但是他发现字符串过长了,于是小 Q 发明了一种压缩算法对字符串中重复的部分进行了压缩,对于字符串中连续的 m 个相同的字符串 S 将会压缩为 [m|S](m 为一个整数且 1<=m<=100),例如字符串 ABCABCABC 将会被压缩为 [3|ABC],现在小 Q 的同学收到了小 Q 发送过来的字符串,你能帮助他进行解压缩么?
输入描述:
输入第一行包含一个字符串 S,代表压缩后的字符串。
S的长度<=1000;
S仅包含大写字母、[、]、|;
解压缩后的字符串长度不超过 100000;
压缩递归层数不超过 10 层;
输出描述:
输出一个字符串,代表解压后的字符串。
输入示例:
HG[3|B[2|CA]]F
输出示例:
HGBCACABCACABCACAF
说明:
HG[3|B[2|CA]]F ->
HG[3|BCACA]F ->
HGBCACABCACABCACAF
个人觉得我的解法很烂,而且太繁琐,但是目前还想不出更好的。代码也写的比较乱 orz. 主要想法是遍历一遍字符串,如果不是特定的压缩模式,直接添加到结果中就好,如果遇到了特殊模式([3|AB]),将该模式提取出来交给另一个函数解码,模式可能递归存在,所以使用一个栈确保提取出正确的模式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// decode pattern like "[3|abc]"
// note: end is included
string PatternDecode(const string& s, size_t beg, size_t end)
{
// the minmal len: [3|a]
// beg=0, end=4
if (end - beg >= 4)
{
string ret;
auto pos_delimiter = s.find('|', beg);
int num_repeats = std::stoi(s.substr(beg+1, pos_delimiter-beg-1));
{
auto pos_left = s.find('[', pos_delimiter);
if (pos_left < end) // has sub-pattern
{
ret += s.substr(pos_delimiter+1, pos_left-pos_delimiter-1);
auto pos_right = s.rfind(']', end-1);
ret += PatternDecode(s, pos_left, pos_right);
ret += s.substr(pos_right+1, end-pos_right-1);
}
else // has not sub-pattern
{
ret += s.substr(pos_delimiter+1, end-pos_delimiter-1);
}
}
string res;
while (num_repeats--)
res += ret;
return res;
}
else
{
throw std::invalid_argument("range too small");
}
}
void Decode(const string& s, string* o)
{
if (s.empty())
throw std::invalid_argument("empty coded string");
stack<size_t> stk;
for (size_t i = 0; i != s.size(); ++i)
{
if (stk.empty() && std::isalpha(s[i]))
{
o->push_back(s[i]);
}
else if (s[i] == '[')
{
stk.push(i);
}
else if (s[i] == ']')
{
// if the stk has only one elem, then the last ']' of
// a pattern is determined, we shall first decode this
// pattern before going on.
if (stk.size() == 1)
{
size_t pattern_beg = stk.top();
o->append(PatternDecode(s, pattern_beg, i));
}
stk.pop();
}
}
}
int main()
{
// io
string input;
cin >> input;
string output;
Decode(input, &output);
cout << output;
return 0;
}
|
题十一:重排并计算逆序数
腾讯 2019 校招
作为程序员的小 Q,它的数列和其他人的不太一样,他有$2^n$个数。老板问了小 Q 一共 m 次,每次给出一个整数$q_i$ (1<=i<=m),要求小 Q 把这些数每$2^{q_i}$分为一组,然后把每组进行翻转,小 Q 想知道每次操作后整个序列中的逆序对个数是多少呢?
例如:
对于序列 1 3 4 2,逆序对有 (4,2), (3,2) 总数量为 2.
翻转之后为 2 4 3 1,逆序对有 (2,1), (4,3), (4,1), (3,1) 总数量为 4.
输入描述:
第一行一个数 n(0<=n<=20)
第二行$2^n$个数,表示初始序列(1<=初始序列<=$10^9$)
第三行一个数 m(1<=m<=$10^6$)
第四行 m 个数表示$q_i$ (0<=$q_i$<=n)
输出描述:
m 行每行一个数表示答案
输入示例:
2
2 1 4 3
4
1 2 0 2
输出示例:
0
6
6
0
说明:
初始序列 2 1 4 3
$2^{q_1} = 2$ -> 第一次:1 2 3 4 -> 逆序对数 0
$2^{q_2} = 4$ -> 第二次:4 3 2 1 -> 逆序对数 6
$2^{q_3} = 1$ -> 第三次:4 3 2 1 -> 逆序对数 6
$2^{q_4} = 4$ -> 第四次:1 2 3 4 -> 逆序对数 0
首先如何计算逆序数,常用的方法是归并排序,可以顺带计算逆序数。但是由于我一开始用的是开销较大的归并,频繁的构造,复制 vector,导致运行超时。后来改成了 inplace 的归并,速度明显提高很多。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
// combine two sorted subseqs
vector<int> merge(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, int* invcount)
{
vector<int> res; // result seq
vector<int>::iterator i = a.begin();
vector<int>::iterator j = b.begin();
while(i != a.end() && j != b.end())
{
if (*i <= *j) res.push_back(*(i++));
if (*i > *j)
{
res.push_back(*(j++));
(*invcount) += (a.end() - i);
}
}
// tail appending ...
if (i == a.end())
{
for(auto iter = j; iter != b.end(); ++iter)
res.push_back(*iter);
}
if (j == b.end())
{
for(auto iter = i; iter != a.end(); ++iter)
res.push_back(*iter);
}
return res;
}
// 归并排序的递归形式
vector<int> mergesort(vector<int>& seq, int* invcount)
{
if (seq.size() == 1) return seq;
else{
// split the seq into two subseqs
int lsize = seq.size() >> 1;
vector<int> tmpl(seq.begin(), seq.begin() + lsize);
vector<int> tmpr(seq.begin() + lsize, seq.end());
vector<int> lseq, rseq;
// recursively slove subproblems
lseq = mergesort(tmpl, invcount);
rseq = mergesort(tmpr, invcount);
return merge(lseq, rseq, invcount);
}
}
// in-place merge sort
namespace inplace
{
/// Merge two sorted range [beg, mid), [mid, end).
void Merge(vector<int>& arr, int beg, int mid, int end, int* invcnt)
{
for (int i = beg, j = mid; i < mid && j < end;)
{
if (arr[i] > arr[j])
{
*invcnt += (mid - i);
std::swap(arr[i], arr[j]);
// rearrange to keep the structure
for (int t = j; t > i+1; --t)
{
std::swap(arr[t], arr[t-1]);
}
++mid;
++j;
}
++i;
}
}
/// Inplace merge sort the range [beg, end).
void MergeSort(vector<int>& arr, int beg, int end, int* invcnt)
{
if (end - beg > 1) // need sort
{
int mid = (beg + end) / 2;
MergeSort(arr, beg, mid, invcnt);
MergeSort(arr, mid, end, invcnt);
Merge(arr, beg, mid, end, invcnt);
}
}
} // namespace inplace
/// reverse the arr by length k
void ReverseBy(vector<int>& arr, int k)
{
for (auto beg = arr.begin(); beg != arr.end(); beg += k)
std::reverse(beg, beg + k);
}
/// compute elapsed time from start_time
inline double TimeElapsed(clock_t start_time)
{
return static_cast<double>(clock()-start_time)
/ CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
}
/// Test wrapper
void UniTest(const vector<int>& numbers,
const vector<int>& qs,
bool inplace)
{
vector<int> dummynum(numbers);
vector<int> buffer(numbers.size());
for (auto e : qs)
{
int invcount = 0;
ReverseBy(dummynum, 1<<e);
buffer.clear();
buffer.assign(dummynum.begin(), dummynum.end());
if (inplace) // use inplace merge sort
inplace::MergeSort(buffer, 0, buffer.size(), &invcount);
else
mergesort(buffer, &invcount);
cout << invcount << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
// io
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> numbers;
for (int i = 0, tmp = 0; i != (1<<n); ++i)
{
cin >> tmp;
numbers.push_back(tmp);
}
int m;
cin >> m;
vector<int> qs;
for (int i = 0, tmp = 0; i != m; ++i)
{
cin >> tmp;
qs.push_back(tmp);
}
// done
clock_t start = clock();
UniTest(numbers, qs, false);
cout << TimeElapsed(start) << "ms for mergesort" << endl;
clock_t start2 = clock();
UniTest(numbers, qs, true);
cout << TimeElapsed(start2) << "ms for inplace mergesort" << endl;
return 0;
}
|
附运行结果,体会一下:
0
6
6
0
0.185ms for mergesort
0
6
6
0
0.068ms for inplace mergesort
差了 3 倍左右!
Josephus Problem
这个问题是以弗拉维奥·约瑟夫命名的,他是 1 世纪的一名犹太历史学家。他在自己的日记中写道,他和他的 40 个战友被罗马军队包围在洞中。他们讨论是自杀还是被俘,最终决定自杀,并以抽签的方式决定谁杀掉谁。约瑟夫斯和另外一个人是最后两个留下的人。约瑟夫斯说服了那个人,他们将向罗马军队投降,不再自杀。约瑟夫斯把他的存活归因于运气或天意,他不知道是哪一个。
——维基百科
描述:人们站在一个等待被处决的圈子里。计数从圆圈中的指定点开始,并沿指定方向围绕圆圈进行。在跳过指定数量的人之后,执行下一个人。对剩下的人重复该过程,从下一个人开始,朝同一方向跳过相同数量的人,直到只剩下一个人,并被释放。(牛客网上类似的题 )
问题即,给定人数、起点、方向和要跳过的数字,选择初始圆圈中的位置以避免被处决。
解法:维基百科 上也有,GeeksforGeeks 还有视频教程。
常见的有两种解法:
显然,假设 n 个人编号:$0,1,2,3,\dots,n-1$. 从 0 号开始报数(报数从 0 开始),报到 m-1 的将被处决,然后从下一个人开始报数。直到剩下最后一个人,赦免之。
第一趟:报到 m 的自然是编号为$(m-1) \mod n$.
接着从 $m \mod n$ 开始报数,接下来又会是谁被处决呢?
等等,先来看看问题是什么,我希望知道幸免者的编号。在 n 个人,报 m 个数的设定下,我希望知道幸免者编号,假设这个编号就是$f(n,m)$, 这里 $f$ 是个神奇的函数,我只要告诉它 n 和 m 它就能告诉我最后幸存者的编号。如果我能找到 $f(n, m)$ 和 $f(n-1, m)$ 的递推关系式,那将是极好的。
在第一趟之后,报数从编号 $k = m \mod n$ 开始,但是此时只有 n-1 个人,我还是想知道幸存者的编号。如果此时将编号重新映射一下,比如:
k -> 0
k+1 -> 1
...
k-2 -> n-2
那么问题就变成了 n-1 个人,从 0 开始报数,报到 m-1 被处决,完完全全成了一个拥有同样结构的问题,但是规模更小了。显然,这个问题的解是 $f(n-1, m)$. 但是呢,我们得到的编号却不是原来的编号了,得把编号还原回去。这很简单,假设得到的编号是 x,那么映射回原编号 y
y = (x+k) mod n
于是,如果我们能够知道 $f(n-1, m)$, 那么
$$
f(n, m) = (f(n-1,m) + m) \mod n.
$$
这就得到了递推公式,接着看一下边界条件,当 n = 1 时, $f(1, m) = 0$; 结束。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| int Josephus(int n, int m)
{
if (n < 1)
throw std::invalid_argument("we need n >= 1");
if (n == 1)
return 0;
return (Josephus(n-1, m) + m) % n;
}
|
扔骰子的期望
拼多多 2019 校招正式批
扔 n 个骰子,第 i 个骰子有可能掷出$X_i$种等概率的不同结果,数字从 1 到$X_i$. 比如$X_i = 2$, 就等可能的出现 1 点或 2 点。所有骰子的结果的最大值将作为最终结果。求最终结果的期望。
输入描述:
第一行一个整数 n,表示 n 个骰子。(1 <= n <= 50)
第二行 n 个整数,表示每个骰子的结果数$X_i$. ($2 \le X_i \le 50$)
输出描述:
输出最终结果的期望,保留两位小数。
示例输入:
2
2 2
示例输出:
1.75
主要考察事件概率的计算。
假设有 3 个骰子,最大点数分别为 2,3,4 点。那么扔 n 个骰子,最终结果为 1 的概率如下
$$
P(1) = \frac{1}{2\times 3 \times 4} = \frac{1}{24}
$$
同理,最终结果为 2,也就是说三个骰子中最大的点数为 2,考虑每个骰子都点数都小于或等于 2 的概率,再减去每个骰子都小于或等于 1 的概率,即为
$$
\begin{gathered}
P(2) = \frac{2\times 2\times 2}{2 \times 3 \times 4} - \frac{1}{2\times 3 \times 4} = \frac{7}{24} \newline
P(3) = \frac{2 \times 3 \times 3}{2 \times 3 \times 4} - \frac{2\times 2\times 2}{2 \times 3 \times 4} = \frac{10}{24} \newline
P(4) = \frac{2 \times 3 \times 4}{2 \times 3 \times 4} - \frac{2\times 3\times 3}{2 \times 3 \times 4} = \frac{6}{24}
\end{gathered}
$$
这就求得了最终结果的所有可能的值对应的概率,可以看出相加为 1,现在可以求期望了。
注意,当要求的点数大于当前骰子的最大点数时,那么该骰子掷出小于该点数的概率为 1. 比如让一个最大点数为 2 的骰子掷出小于 3 的点数,显然概率为 1.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<double> Distribution(const vector<int>& die_ranges, int support)
{
vector<double> probs;
for (int i = 1; i <= support; ++i)
{
double pprob = 1.0; // for previous prob
double prob = 1.0; // for current prob
for (auto e : die_ranges)
{
pprob *= min(double(i-1) / double(e), 1.0);
prob *= min(double(i) / double(e), 1.0);
}
probs.push_back(prob - pprob);
}
return probs;
}
int main()
{
int num_die;
cin >> num_die;
int maxpoint = 0;
vector<int> die_ranges;
for (int i = 0, tmp; i != num_die; ++i)
{
cin >> tmp;
if (tmp > maxpoint)
maxpoint = tmp;
die_ranges.push_back(tmp);
}
// io done
vector<double> probs = Distribution(die_ranges, maxpoint);
double expectation = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i <= maxpoint; ++i)
{
expectation += (probs[i-1] * i);
}
printf("%.2f", expectation);
return 0;
}
|
递增二叉树
网易互娱 2020 校招正式批
给定一颗二叉树,每个节点又一个正整数权值。若一棵二叉树,每一层的节点权值之和都严格小于下一层的节点权值之和,则称这颗二叉树为递增二叉树。现在给你一颗二叉树,请判断它是否是递增二叉树。
输入描述:
输入的第一行是一个正整数 T(0 < T <= 50)。接下来有 T 组样例,对于每组样例,输入的第一行是一个正整数 N,表示树的节点个数(0 < N <= 100,节点编号为 0 到 N-1)。接下来是 N 行,第 k 行表示编号为 k 的节点,输入格式为:VALUE LEFT RIGHT,其中 VALUE 表示其权值,是一个不超过 5000 的自然数;LEFT 和 RIGHT 分别表示该节点的左孩子编号和右孩子编号。如果其不存在左孩子或右孩子,则 LEFT 或 RIGHT 为 -1.
输出描述:
对于每一组样例,输出一个字符串。如果该二叉树是一颗递增树,则输出 YES,否则输出 NO。
样例输入:
2
8
2 -1 -1
1 5 3
4 -1 6
2 -1 -1
3 0 2
2 4 7
7 -1 -1
2 -1 -1
8
21 6 -1
52 4 -1
80 0 3
31 7 -1
21 -1 -1
59 -1 -1
50 5 -1
48 -1 1
样例输出:
YES
NO
这题最恶心的是输入格式,居然不是直接给一颗建好的二叉树的根节点,而是给数据让你自己建树。处理输入还比较麻烦,首先每个节点都有编号,得先存起来,然后一个一个构造节点,然后再连接起来,关键是连好以后,头节点在哪?还得找一下,最后的判断,实际上是二叉树的层次遍历,遍历得到一个向量,判断是否为严格单调递增即可。
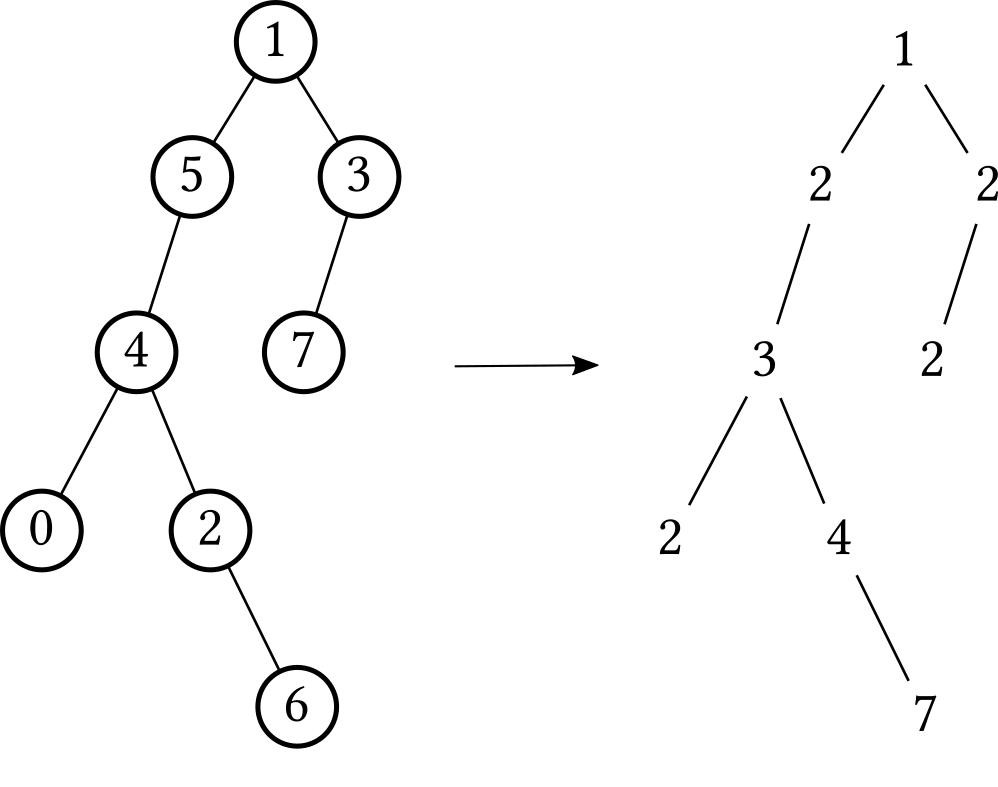
上图是第一个样例画出来的二叉树,左边圆圈中对应的是节点编号,右边的数字是节点的权值。要画这棵树,首先画左边的编号之间的连接图,然后把对应编号换作节点的权值即可。那么头节点在哪呢?入度为 0 的就是了!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int v)
: val(v), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
struct NodeInfo
{
TreeNode* pnode;
int left;
int right;
NodeInfo(TreeNode* p, int l, int r):
pnode(p), left(l), right(r) {}
};
// build the tree and return the root
TreeNode* BuildTree(vector<NodeInfo>& nodes)
{
vector<int> counts(nodes.size(), 0);
// link
for (size_t i = 0; i != nodes.size(); ++i)
{
int left = nodes[i].left;
int right = nodes[i].right;
if (left != -1)
{
nodes[i].pnode->left = nodes[left].pnode;
++counts[left];
}
if (right != -1)
{
nodes[i].pnode->right = nodes[right].pnode;
++counts[right];
}
}
// find root
for (size_t i = 0; i != counts.size(); ++i)
{
if (counts[i] == 0)
return nodes[i].pnode;
}
throw std::logic_error("no root");
}
// Is the tree a increasing tree?
bool IsIncrTree(TreeNode* root)
{
if (!root) return false;
vector<vector<int>> mat;
// tranverse the tree by layer
std::function<void(TreeNode*, int)> layer_travel;
layer_travel =
[&mat, &layer_travel](TreeNode* p, int depth) mutable
{
if (p == nullptr) return;
if ((int)mat.size() == depth)
mat.emplace_back(vector<int>());
mat[depth].push_back(p->val);
layer_travel(p->left, depth + 1);
layer_travel(p->right, depth + 1);
};
layer_travel(root, 0);
vector<int> sums;
for (auto& row : mat)
{
int sum = 0;
for (auto c : row) sum += c;
sums.push_back(sum);
}
for (size_t i = 1; i != sums.size(); ++i)
{
if (sums[i-1] >= sums[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int num_test;
cin >> num_test;
for (int num_nodes = 0; num_test--;)
{
cin >> num_nodes;
vector<NodeInfo> nodes;
while (num_nodes--)
{
int v, l, r;
cin >> v >> l >> r;
TreeNode* p = new TreeNode(v);
nodes.emplace_back(p, l, r);
}
TreeNode* root = BuildTree(nodes);
if (IsIncrTree(root))
cout << "YES\n";
else
cout << "NO\n";
// memory clean
for (auto& node : nodes)
{
delete node.pnode;
node.pnode = nullptr;
}
} // nodes released
return 0;
}
|
经过棋盘的最小开销
58 同城 2020 校招
现有一个地图,由横线与竖线组成(参考围棋棋盘),起点在左上角,终点在右下角。每次行走只能沿线移动到相邻的点,每走一步产生一个开销。计算从起点到终点的最小开销为多少。
输入描述:
$m \times n$ 的地图表示如下
3
3
1 3 4
2 1 2
4 3 1
其中 m=3,n=3 表示 3*3 的矩阵
行走路径为:下>右>右>下
输出描述:
路径总长:1+2+1+2+1=7
动态规划入门题,可惜我当时碰到 DP 就慌,而且只会递归 DP,自顶向下,复杂度会高很多。
假设用一个矩阵,名字就叫 dp,表示最优结果。dp(i,j) 表示从起点到坐标 (i,j) 的最小开销。很容易得到递推关系:
$$
\text{dp}(i, j) =
\begin{cases}
\text{map}(i,j) + \min(\text{dp}(i, j-1), \text{dp}(i-1, j)) & i, j > 0\newline
\sum_{x=0}^{j-1} \text{map}(i, j) & i = 0 \newline
\sum_{x=1}^{i-1} \text{map}(i, j) & j = 0
\end{cases}.
$$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// greedy
int MinCost(const vector<vector<int>>& mat)
{
int row = static_cast<int>(mat.size());
int col = static_cast<int>(mat[0].size());
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int ret = 0;
while (i < row-1 && j < col-1)
{
ret += mat[i][j];
if (mat[i+1][j] < mat[i][j+1]) ++i;
else ++j;
}
if (i == row-1)
{
for (int x = j; x <= col-1; ++x)
ret += mat[i][x];
}
else
{
for (int x = i; x <= row-1; ++x)
ret += mat[x][j];
}
return ret;
}
// dynamic programming
int mincost(const vector<vector<int>>& mat)
{
int row = static_cast<int>(mat.size());
int col = static_cast<int>(mat[0].size());
vector<vector<int>> dp(row, vector<int>(col, 0));
// initialize
dp[0][0] = mat[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < row; ++i)
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0] + mat[i][0];
for (int j = 1; j < col; ++j)
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1] + mat[0][j];
for (int i = 1; i < row; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j < col; ++j)
{
dp[i][j] = mat[i][j] + min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[row-1][col-1];
}
int main()
{
int num_rows, num_cols;
cin >> num_rows >> num_cols;
vector<vector<int>> mat(num_rows, vector<int>(num_cols, 0));
for (int i = 0; i != num_rows; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0, x; j != num_cols; ++j)
{
cin >> x;
mat[i][j] = x;
}
}
// io done
cout << mincost(mat);
return 0;
}
|
出列的顺序(类约瑟夫环)
VIVO 2020 校招正式批
将 N 个人排成一排,从第一个人开始报数,如果报数是 M 的倍数就出列,报道队尾后则回到队头继续报数,直到所有人都出列。
输入描述:
输入 2 个正整数,空格分隔,第一个代表人数 N,第二个代表 M。
输出描述:
输出一个数组,每个数据表示原来在队列中的位置,用空格隔开,表示出列顺序
输入实例:
6 3
输出示例:
3 6 4 2 5 1
说明:6 个人排成一排,原始位置编号 1-6,最终输出为 3 6 4 2 5 1,
表示的是原来编号为 3 的第一个出列,编号为 1 的最后出列。
思路:类似于约瑟夫环,使用链表模拟整个过程即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int val;
Node* next;
Node(int n): val(n), next(nullptr) {}
};
vector<int> ToQueue(int num_employee, int mod)
{
if (num_employee == 0) return vector<int>();
if (num_employee == 1) return vector<int>(1, 1);
// else num_employee >= 2
// build list
vector<Node*> nodes;
for (int i = 1; i <= num_employee; ++i)
{
Node* p = new Node(i);
nodes.push_back(p);
}
for (size_t i = 1; i != nodes.size(); ++i)
{
nodes[i-1]->next = nodes[i];
}
nodes.back()->next = nodes.front();
Node* prev = nodes.back();
Node* cur = nodes.front();
vector<int> ret;
for (int count = 1; cur->next != cur; ++count)
{
if (count % mod == 0)
{
ret.push_back(cur->val);
prev->next = cur->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
ret.push_back(cur->val);
// memory clean
for (Node* p : nodes) delete p;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int num_employee, mod;
cin >> num_employee >> mod;
for (auto e : ToQueue(num_employee, mod))
cout << e << " ";
return 0;
}
|
最短通行时间
度小满金融 2020 校招
有 N 辆车要陆续通过一座最大承重为 W 的桥,其中第 i 辆车的重量为 w[i], 过桥时间为 t[i]. 要求:第辆车上桥时间不早于第 i-1 辆车上桥的时间;i 任意时刻桥上所有车辆的总重量不超过 W。那么,所有车辆都通过这座桥的所需的最短时间是多少?
输入:
第一行输入两个整数 N,W(1 <= N, W <= 100000)
第二行输入 N 个整数 w[1] 到 w[N](1 <= w[i] <= W)
第三行输入 N 个整数 t[1] 到 t[N](1 <= t[i] <= 10000)
4 2
1 1 1 1
2 1 2 2
输出:
4
干就完了,模拟!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int MinTime(const vector<int>& car_weights,
vector<int>& pass_times,
const int max_weight)
{
int len = car_weights.size();
int elapsed_time = 0;
int cur = 0;
int w = max_weight;
for (;;)
{
int start = cur;
while (cur < len && w >= car_weights[cur])
{
w -= car_weights[cur++];
}
if (cur >= len) // reach the last car
{
elapsed_time +=
*std::max_element(pass_times.begin() + start, pass_times.end());
return elapsed_time;
}
else
{
// each time a car passed, some other car may board the bridge
int mintime_idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cur; ++i)
{
if (pass_times[mintime_idx] > pass_times[i] && pass_times[i] != 0)
mintime_idx = i;
}
elapsed_time += pass_times[mintime_idx];
for (int i = 0; i < cur; ++i) // update time
pass_times[i] = max(pass_times[i] - pass_times[mintime_idx], 0);
// car @mintime_idx has passed, now @w may be free to pass a new car
w += car_weights[mintime_idx];
}
}
}
int main()
{
int num_car, max_weight;
cin >> num_car >> max_weight;
vector<int> car_weights;
for (int n = num_car, w; n--;)
{
cin >> w;
car_weights.push_back(w);
}
vector<int> pass_times;
for (int n = num_car, t; n--;)
{
cin >> t;
pass_times.push_back(t);
}
// io done
cout << MinTime(car_weights, pass_times, max_weight);
return 0;
}
|
数据结构相关
大部分出自 《剑指 Offer》
打印二叉树最右边的节点
给定一个二叉树,打印其每层最右边的节点的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
using std::vector;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int _val):
val(_val), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) { }
};
// print the right-most node of each layer of a tree.
vector<int> PrintRightMost(TreeNode* root)
{
// - time: O(N), where N is #TreeNodes
// - space: O(N + logN)
if (!root) return vector<int>();
vector<vector<int>> mat;
std::function<void(TreeNode*, int)> layer_travel =
[&mat, &layer_travel](TreeNode* p, int depth)
{
if (p == nullptr) return;
if (depth == (int)mat.size())
mat.emplace_back(vector<int>());
mat[depth].push_back(p->val);
layer_travel(p->left, depth + 1);
layer_travel(p->right, depth + 1);
};
vector<int> ret;
for (auto &row : mat) ret.push_back(row.back());
return ret;
}
|
使用两个栈构造一个队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| /*
* Basic idea:
* 1. the top of stack1 as queue rear
* 2. the top of stack2 as queue front
*/
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Queue {
private:
stack<int> s1;
stack<int> s2;
public:
void push(int _node) {
s1.push(_node);
}
int pop() {
if (s2.empty()) {
while (!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.top());
s1.pop();
}
}
int res = s2.top();
s2.pop();
return res;
}
};
|
使用两个队列构造一个栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| /*
* 1. queue2 as a auxiliary storage
* 2. push: push to the rear of queue1
* 3. pop:
* 3.1. quque1 has only one element, pop it
* 3.2. pop the elements of queue1, push them to queue2
* till queue1 has exactly one left, pop it
* then pop elems of queue2 push to queue1
*/
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class Stack {
private:
queue<int> q1;
queue<int> q2;
public:
void push(int _node) {
q1.push(_node);
}
int pop() {
while (q1.size() != 1) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
int res = q1.front();
q1.pop();
while (!q2.empty()) {
q1.push(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
|
反向打印链表
给定一个单链表,反向打印每个节点的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| /*
* 1. use stack
* 2. use recursion
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class ListNode {
public:
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> ret;
// boundary case
if (head == nullptr) return ret;
stack<int> s;
for (auto p = head; p != nullptr; p = p -> next) {
s.push(p -> val);
}
while (!s.empty()) {
ret.push_back(s.top());
s.pop();
}
return ret;
}
// recursive needs a member variable
// use recursion stack, tricky
vector<int> arr;
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
if (head) {
reversePrint(head -> next);
arr.push_back(head -> val);
}
return arr;
}
/*
* Consider the closure, at one recursive step,
* what I should do? Let's drop all the details,
* just look one recursive step.
* What had I done?
* Oh gee, I see if the head is not null,
* I must push the value to the vector,
* but before this, I should take a look at
* `head -> next`, since I have to push
* the tail first. So which one can help me
* do this? Yes, the function itself! Then
* after I have addressed the tail, now I'm
* going to push current value to the vector.
* That's all I need!
* The key is you work in one recursive step, and
* form a closure for the next, and do not forget
* the base case (stopping rules). That how
* recursion runs! And you are free of those
* confusing details.
*/
};
|
判断可能的出栈序列
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列 1,2,3,4,5 是某栈的压入顺序,序列 4,5,3,2,1 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 4,3,5,1,2 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| /*
* The idea is I push all elems of `pushV` into
* a stack `s`, simultaneously, I track if the elems
* of `popV` equal to the `s.top()`. If it is, I will
* pop a elem from the stack and track the next elem
* of `popV` till a mismatch. Then I'll continue to push
* elems into the stack.
*
* When I run out all elems of `pushV`, I check if the
* stack is empty, if it is, then the `popV` should be
* a possible pop sequence or vice versa.
*
* Credit: https://www.nowcoder.com/profile/248554
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int> pushV, vector<int> popV) {
// border case
if (pushV.size() == 0) return false;
stack<int> s;
auto i = 0, j = 0;
while (i != pushV.size()) {
s.push(pushV[i++]);
// KEY POINT here
while (!s.empty()
&& s.top() == popV[j]
&& j != popV.size()) {
s.pop();
j++;
}
}
return s.empty();
}
};
// test
int main() {
vector<int> pushV = {1,2,3,4,5};
vector<int> popV = {4,5,3,2,1};
cout << Solution().IsPopOrder(pushV, popV);
return 0;
}
|
括号匹配
原题:https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-parentheses/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) { // 此解法还是比较 elegant 的
stack<char> stk;
for (auto &c : s)
{
switch (c)
{
case '{': stk.push('}'); break;
case '(': stk.push(')'); break;
case '[': stk.push(']'); break;
default:
{
if (stk.empty() || c != stk.top()) // 巧妙地判断了 stk 非空
return false;
else
stk.pop();
}
}
}
return stk.empty();
}
};
|
二叉树的层次遍历
给定一颗二叉树,按每一层从左往右的顺序遍历。(队列的典型应用)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| /*
* This is a typical application of queue.
* With the help of a queue, you can easily do this.
*
* You can also use recursion.
*/
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode {
public:
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> HierarchicalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
// further error handle
return vector<int>();
}
vector<int> ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
auto cur = q.front();
// from left to right push the current
// root's children to the queue
if (cur -> left) q.push(cur -> left);
if (cur -> right) q.push(cur -> right);
ret.push_back(cur -> val);
q.pop();
}
return ret;
}
/// recursive
vector<vector<int> > layerTraverse(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return ret;
build(root, 0);
return ret;
}
// recursion needs a member variable
vector<vector<int> > ret;
void build(TreeNode* p, int depth) {
if (p == nullptr) return;
if (ret.size() == depth)
ret.push_back(vector<int>());
ret[depth].push_back(p -> val); // use depth to track layer
build(p -> left, depth + 1);
build(p -> right, depth + 1);
}
};
|
求整数的二进制表示中“1”的个数
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中 1 的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| /*
* `n` and `n-1` are the same from high bit position
* to low, they differs from the last bit of 1 of n,
* let's name it x. Have a look from x to the lowest
* bit position,
* n: 010101000
* & x <--- position x
* n-1: 010100111
* ---------------
* 010100000 <--- n&(n-1)
* It erases the last bit of 1 in n!!!
*
* This is why the following procedure will work. :)
*/
#include <iostream>
int NumOf1(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
while (n) {
n = n & (n-1);
++cnt;
}
return cnt;
}
int main() {
int N = 0;
std::cin >> N;
std::cout << NumOf1(N);
return 0;
}
|
不可描述
求出 113 的整数中 1 出现的次数,并算出 1001300 的整数中 1 出现的次数?为此他特别数了一下 1~13 中包含 1 的数字有
1、10、11、12、13
因此共出现 6 次,但是对于后面问题他就没辙了。ACMer 希望你们帮帮他,并把问题更加普遍化,可以很快的求出任意非负整数区间中 1 出现的次数(从 1 到 n 中 1 出现的次数)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| /*
* Credits: unknown
*
* Idea:
* 1) Focus exactly one decimal position, calculate the
* number of ones.
* 2) Run out from lowest to highest position, add them
* together, it's the answer.
*
* Imaging the numbers from 1 to n sits in a line in
* front of you. Now you're required to calculates all
* the ones in the sequence. A basic way is that, each
* time I focus on the same digit pos, and count all
* ones in that pos. Next time I focus on another pos.
* And I sum them all together, finally got the answer.
*
* See how can we count the num of ones in a specific
* decimal pos? Let's do that! Suppose N = 301563.
*
* Step 1.
* Now I focus the hundred position, and split N into `a`
* and `b`, where
*
* a = ceil(N / 100) = 3015
* b = N % 100 = 63
*
* 1). There are (a / 10 + 1) = 302 hits of one
* 2). Each of length 100
* 3). Totally (a/10 + 1) * 100 hits of one
*
* Let me explain a little:
* (000-301)5(00-99) -> (000-301)1(00-99)
*
* The digits above hundred pos have 302 variants, and
* the digits under hundred pos has 100 variants, thus
* gives a total (a/10 + 1) * 100.
*
* Step 2.
* This time I focus on thousand pos, and now
*
* a = N / 1,000 = 301
* b = N % 1,000 = 563
*
* 1). There are (a/10) = 30 hits of one
* 2). Each of length 1000
* 3). And a tail hits of 564
*
* (00-29)1(000-999) + 301(000-563)
* This gives 30 * 1000 + 564 = (a/10)*1000+(b+1)
*
* Step 3.
* Now move to ten thousand pos, with
*
* a = N / 10,000 = 30
* b = N % 10,000 = 1563
*
* 1). There are total (a/10)=3 hit
* 2). Each of length 10,000
*
* (0-2)1(0000-9999)
* gives 3 * 10,000 = (a/10).
*
* That's all 3 cases. Let's write!
*/
class Solution {
public:
int NumOnes(int n) {
int ones = 0;
for (long long m = 1; m <= n; m *= 10) {
ones +=
/*
* this covers case 1 & 3
* since (a+8)/10 = a/10 + 1 if a%10 >= 2
* (a+8)/10 = a/10 if a%10 == 0
*/
(n/m + 8) / 10 * m
+
// case 2
(n/m % 10 == 1) * (n%m + 1);
}
return ones;
}
};
|
K 轮换
原题:https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-array/
Given an array, rotate the array to the right by k steps, where k is non-negative.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] and k = 3
Output: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
rotate 2 steps to the right: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
rotate 3 steps to the right: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input: [-1,-100,3,99] and k = 2
Output: [3,99,-1,-100]
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: [99,-1,-100,3]
rotate 2 steps to the right: [3,99,-1,-100]
Note:
- Try to come up as many solutions as you can, there are at least 3 different ways to solve this problem.
- Could you do it in-place with O(1) extra space?
提供三种方法:第一种,效率最低,因为 vector 从头插入元素开销很大;第二种,花费额外的空间,来降低时间开销;第三种,挺好的,std::reverse 用的是首尾交换元素,无额外空间开销。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
#if false // method 1.
if (k == 0) return;
nums.insert(nums.begin(), nums.back());
nums.pop_back();
rotate(nums, k-1);
#elif false // method 2.
vector<int> dummy(nums);
for (int i = 0; i != dummy.size(); ++i)
{
nums[(i+k) % nums.size()] = dummy[i];
}
#elif true // method 3.
k %= nums.size();
std::reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end());
std::reverse(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + k);
std::reverse(nums.begin() + k, nums.end());
#endif
}
};
|
Move zeros
原题:https://leetcode.com/problems/move-zeroes/
Given an array nums, write a function to move all 0’s to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
Example:
Input: [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]
Note:
- You must do this in-place without making a copy of the array.
- Minimize the total number of operations.
思路:记录数字 0 出现的个数 count。如果当前数字是 0,给 count 加一;如果不是 0,将这个值往前挪 count 位。最后将最后 count 个元素置 0.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() < 2) return;
// c.f. https://leetcode.com/explore/interview/card/top-interview-questions-easy/92/array/727/
int numzeros = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != nums.size(); ++i)
{
if (nums[i] == 0)
++numzeros;
else
nums[i-numzeros] = nums[i];
}
// set the tails to 0
while (numzeros)
{
nums[nums.size() - numzeros] = 0;
--numzeros;
}
}
};
|
Kth Largest Element in an Array
From: LeetCode125.
Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Example 1:
Input: [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] and k = 4
Output: 4
Note: You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ array’s length.
思路:利用快排的 partition 思想,每次选取一个 pivot,将数组分为小于 pivot 和大于 pivot 的两部分。此时 pivot 的 index 就是排好序之后的 index,与 k 相比,如果出较小,则在后半部分(大于 pivot)再次划分,如果较大,则在前半部分划分。直到划分出来的 pivot 的 index 等于 k。还要注意的是,这样找出来的是第 k 小,用数组长度减一下,才是第 k 大,注意 index 的变换。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
// from 王小康:快排 partition 知道吧?
// 就一刀一刀地劈开,劈一次你知道 pivot 的 index,
// 如果比 k 小,继续在右边劈,如果比 k 大,就在左边劈!
if (nums.empty()) throw std::invalid_argument("empty arr");
if (nums.size() == 1) return nums.front();
// else @nums has >= 2 elems
int mid = Partition(nums, 0, nums.size());
k = nums.size() - k; // kth large = len+1-k small
while (mid != k)
{
if (mid < k)
mid = Partition(nums, mid + 1, nums.size());
else
mid = Partition(nums, 0, mid);
}
return nums[mid];
}
size_t Partition(vector<int>& arr, size_t beg, size_t end)
{
size_t pivot = beg;
size_t i = pivot + 1;
for (auto j = pivot + 1; j < end; ++j)
{
if (arr[j] < arr[pivot])
{
std::swap(arr[j], arr[i]);
++i;
}
}
std::swap(arr[i-1], arr[pivot]);
return i - 1;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> nums = {3,2,1,5,6,4};
Solution so;
cout << so.findKthLargest(nums, 2);
return 0;
}
|
最大连续子列
From: LeetCode53.
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
Example:
Input: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
Output: 6
Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
设置两个变量,一个记录当前连加的值,另一个记录目前位置最大连续子序列,迭代更新。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| int MaxSubArray(const vector<int>& arr)
{
int max_so_far = INT_MIN;
int sum = 0;
for (int e : arr)
{
if (sum > 0)
sum += e;
else
sum = e;
max_so_far = max(max_so_far, sum);
}
return max_so_far;
}
|


